Clinical Studies
Multiple Sclerosis
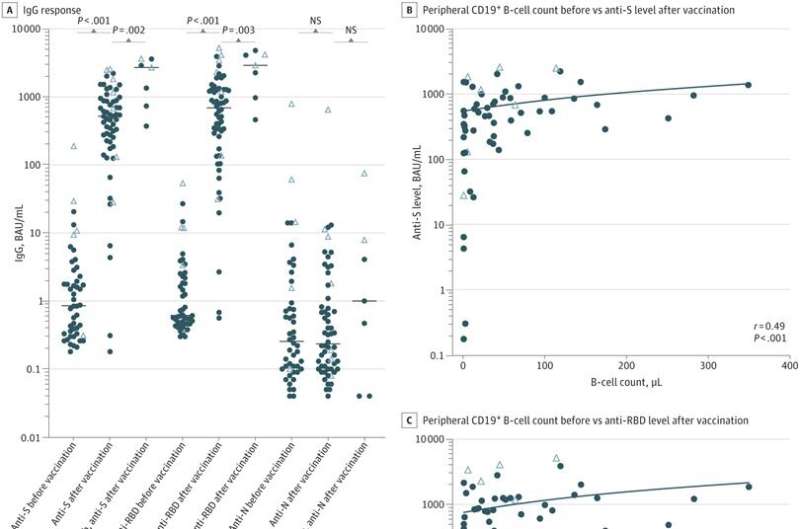
Multiple sclerosis patients with higher B cell counts found to have a better vaccine response
Multiple sclerosis (MS) patients treated with Rituximab have better responses to the COVID-19 vaccine if they have higher B cell counts. This is the finding of a study from Uppsala University published in the journal JAMA Network Open. In patients with B cell counts...
Clinical trial yields fewer relapses in multiple sclerosis patients treated with off-label drug
Patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) treated with the drug rituximab had a significantly lower risk of relapse compared with MS patients receiving standard treatment. This has been shown in a phase 3 clinical trial by researchers at Karolinska Institutet and Danderyd...
Alzheimer’s
Cellular waste disposal study provides new insights into Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s
A 'waste collection' tidies up our cells. If something does not go according to plan, serious diseases such as Alzheimer's or Parkinson's may develop. Molecular biologist Sascha Martens from the University of Vienna together with international partners—researchers of...

Study finds why women with Alzheimer’s disease experience faster memory decline
Alzheimer's disease is the world's most common neurodegenerative disease, affecting the memory, thinking and behavior of over 40 million people worldwide. It accounts for 60 to 70 percent of dementia cases and is known to affect more women than men. A joint study by...
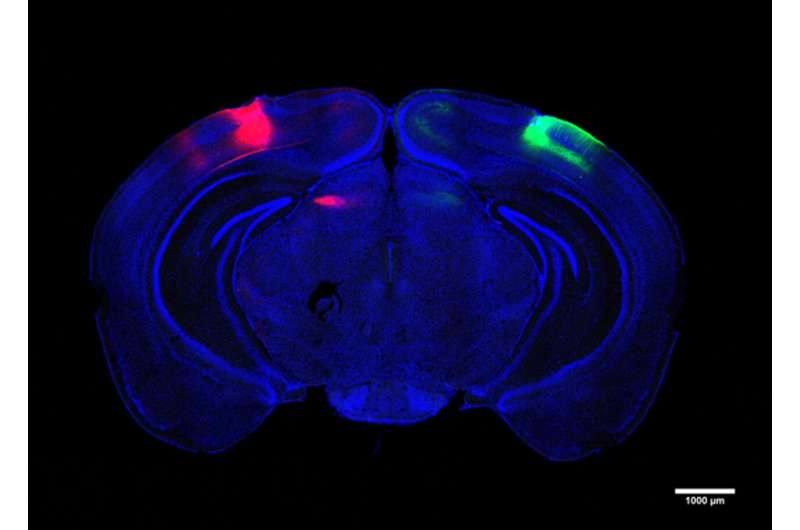
When Alzheimer’s degrades cells that cross hemispheres, visual memory suffers
A new MIT study finds that Alzheimer's disease disrupts at least one form of visual memory by degrading a newly identified circuit that connects the vision processing centers of each brain hemisphere. The results of the study, published in Neuron by a research team...
Parkinson’s disease

Protein test could lead to earlier and better diagnosis of Parkinson’s
Scientists at the Oxford Parkinson's Disease Centre (OPDC) have been able to use a highly-sensitive method called α-synuclein real-time quaking-induced conversion (αSyn-RT-QuIC) to observe the clumping of alpha-synuclein in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) taken from...

Cellular waste disposal study provides new insights into Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s
A 'waste collection' tidies up our cells. If something does not go according to plan, serious diseases such as Alzheimer's or Parkinson's may develop. Molecular biologist Sascha Martens from the University of Vienna together with international partners—researchers of...
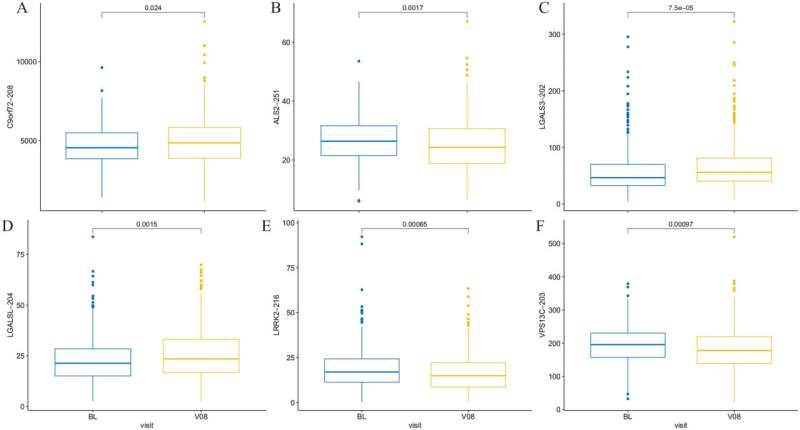
Study identifies new DNA clues for Parkinson’s disease risk
Findings of a new Parkinson's disease study have opened an exciting avenue for developing therapeutics to intervene in the progression of this common movement disorder.The feature article in Experimental Biology and Medicine contributes to understanding of genetic...

Aerobic Exercise Positively Alters Parkinson’s Brain
Getting regular exercise is essential to managing Parkinson’s disease (PD). It is well established that exercise promotes aerobic conditioning, strength, balance, flexibility and mobility, which can substantially improve overall quality of life. Multiple...
Migraines

Largest genetic study of migraines to date reveals new genetic risk factors
An international consortium of leading migraine scientists identified more than 120 regions of the genome that are connected to risk of migraine. The groundbreaking study helps researchers better understand the biological basis of migraine and its subtypes and could...

Migraines caused by alterations in metabolite levels
Migraines are a pain in the head and in the hip pocket, but newly discovered genetic causes by QUT researchers could lead the way to new preventative drugs and therapies. Genetic analyses findings were published in The American Journal of Human Genetics by Professor...

Genetic study identifies migraine causes and promising therapeutic targets
QUT genetic researchers have found blood proteins that cause migraine and have a shared link with Alzheimer's disease that could potentially be prevented by repurposing existing therapeutics. Findings from the genetic analyses were published in Nature...
